Georgia (country)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the Eurasian country. For the U.S. state, see Georgia (U.S. state). For other uses, see Georgia (disambiguation)
| Georgia
საქართველო
Sakartvelo | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: ძალა ერთობაშია Dzala Ertobashia Strength is in Unity | ||||||
| Anthem: თავისუფლება Tavisupleba Freedom | ||||||
|
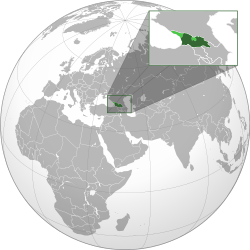
Georgia proper shown in dark green; areas outside of Georgian control but claimed as part of its sovereign territory shown in light green.
| ||||||
| Capital and largest city | Tbilisi[a] 41°43′N 44°47′E | |||||
| Official languages | Georgian[1] | |||||
| Spoken languages[2] |
| |||||
| Ethnic groups(2002) |
| |||||
| Demonym | Georgian | |||||
| Government | Unitary semi-presidentialrepublic[3] | |||||
| • | President | Giorgi Margvelashvili | ||||
| • | Prime Minister | Giorgi Kvirikashvili | ||||
| • | Speaker of the Parliament | David Usupashvili | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||
| Independence | ||||||
| • | Kingdom of Colchis | 13th century–164 BC | ||||
| • | Kingdom of Diaokhi | 12th century BC–8th century BC | ||||
| • | Kingdom of Iberia | 302 BC–580 AD | ||||
| • | Kingdom of Lazica-Egrisi | 131 BC–697 AD | ||||
| • | Principality of Iberia | 580-880 AD | ||||
| • | Kingdom of Abkhazia | 767-1014 AD | ||||
| • | Kingdom of Georgia | 1008 | ||||
| • | Russian Empireoccupation | 12 September 1801 | ||||
| • | from Russian Empire | 26 May 1918 | ||||
| • | Soviet re-conquest | 25 February 1921 | ||||
| • | from Soviet Union
Declared
Finalized | 9 April 1991 25 December 1991 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | Total | 69,420 km2 (120th) 26,911 sq mi | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | 2015 estimate | 3,729,500[4] (131st) | ||||
| • | 2014 census | 3,729,635[5] | ||||
| • | Density | 53.5/km2 (137th) 138.6/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $37.27 billion[2] (117th) | ||||
| • | Per capita | $8,223 | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2015 estimate | |||||
| • | Total | $16.535 billion[6] | ||||
| • | Per capita | $4,719[6] | ||||
| Gini (2013) | 40.0[7] medium | |||||
| HDI (2014) | high · 76th | |||||
| Currency | Lari ( | |||||
| Time zone | GET (UTC+4) | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | +995 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | GE | |||||
| Internet TLD | .ge .გე | |||||
| a. | ^ The Seat of Parliament is in Kutaisi | |||||
Georgia ( i/ˈdʒɔːrdʒə/; Georgian: საქართველო, tr. Sakartvelo, IPA: [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] (
i/ˈdʒɔːrdʒə/; Georgian: საქართველო, tr. Sakartvelo, IPA: [sɑkʰɑrtʰvɛlɔ] ( listen)) is a country in Eurasia, located on the crossroads of Eastern Europe and West Asia. Nestled between the Greater Caucasusand Lesser Caucasus mountain ranges, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its 2015 population is about 3.75 million. Georgia is a unitary, semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through arepresentative democracy.
listen)) is a country in Eurasia, located on the crossroads of Eastern Europe and West Asia. Nestled between the Greater Caucasusand Lesser Caucasus mountain ranges, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north and northeast by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its 2015 population is about 3.75 million. Georgia is a unitary, semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through arepresentative democracy.
During classical antiquity, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia. The kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia adopted Christianity as their state religion in the early 4th century, leading to the decline and elimination of previously dominant paganism, Zoroastrianism, and Mithraism. A unified Kingdom of Georgia reached the peak of its political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV andQueen Tamar from the late 11th to the early 13th centuries. Thereafter and throughout the early modern period Georgia became fractured and fell into decline due to the onslaught of various hostile empires, including the Mongols, the Ottoman Empire, and successive dynasties of Iran. In 1783, the eastern Georgian kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti forged an ill-fated alliance with the Russian Empire, which led to the gradual annexation of Georgia by Russia starting in 1801. After a brief period of independence following the Russian Revolution of 1917, the first Georgian Republic was occupied by Soviet Russia in 1921, and absorbed into the Soviet Unionas the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1922. After restoring its independence in 1991, post-communist Georgia suffered from a civil unrest and economic crisis for most of the 1990s. After a peaceful change of power in the Rose Revolution of 2003, Georgia pursued a strongly pro-Western foreign policy, introducing a series of political and economic reforms.
Georgia is a member of the Council of Europe and the GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development. It contains two de facto independent regions, Abkhazia and South Ossetia, which gained limited international recognition after the 2008 Russo-Georgian War. Georgia and a major part of the international community consider the regions to be part of Georgia's sovereign territory under Russian military occupation.[9]